“(SKU:ELB040501)电子积木I2C存储模块 24C32存储EEPROM模块”的版本间的差异
来自YwRobot Studio Wiki
YWrobot WM(讨论 | 贡献) (创建页面,内容为“电子积木I2C存储模块 24C32存储EEPROM模块 <br> ==产品参数== *尺...”) |
(→样例代码) |
||
| 第18行: | 第18行: | ||
===样例代码=== | ===样例代码=== | ||
<pre style="color:blue"> | <pre style="color:blue"> | ||
| + | #include <Wire.h> | ||
| + | #define EEPROM_ADDR 0x57 // I2C Buss address of 24LC256 256K EEPROM | ||
| + | void setup() { | ||
| + | Wire.begin(); // join I2C bus (address optional for master) | ||
| + | Serial.begin(9600); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // TESTS FOR EACH FUNCTION BEGIN HERE | ||
| + | Serial.println("Writing Test:"); | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { // loop for first 20 slots | ||
| + | i2c_eeprom_write_byte(EEPROM_ADDR, i, i + 65); // write address + 65 A or 97 a | ||
| + | Serial.print(". "); | ||
| + | delay(10); // NEED THIS DELAY! | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | Serial.println(""); | ||
| + | delay(500); | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serial.println("Reading Test:"); | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { // loop for first 20 slots | ||
| + | Serial.print(i2c_eeprom_read_byte(EEPROM_ADDR, i)); | ||
| + | Serial.print(" "); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | // setup for page tests . . . | ||
| + | byte PageData[30]; // array that will hold test data for a page | ||
| + | byte PageRead[30]; // array that will hold result of data for a page | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) { // zero both arrays for next test | ||
| + | PageData[i] = 0; | ||
| + | PageRead[i] = 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | Serial.println(""); | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) PageData[i] = i + 33; // fill up array for next test char 33 = ! | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serial.println("Writing Page Test:"); | ||
| + | i2c_eeprom_write_page(EEPROM_ADDR, 100, PageData, 28 ); // 28 bytes/page is max | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serial.println("Reading Page Test:"); | ||
| + | i2c_eeprom_read_buffer( EEPROM_ADDR, 100, PageRead, 28); | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < 28; i++) { | ||
| + | Serial.print(PageRead[i]); // display the array read | ||
| + | Serial.print(" "); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | void loop() | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | void i2c_eeprom_write_byte( int deviceaddress, unsigned int eeaddress, byte data ) { | ||
| + | int rdata = data; | ||
| + | Wire.beginTransmission(deviceaddress); | ||
| + | Wire.write((int)(eeaddress >> 8)); // Address High Byte | ||
| + | Wire.write((int)(eeaddress & 0xFF)); // Address Low Byte | ||
| + | Wire.write(rdata); | ||
| + | Wire.endTransmission(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Address is a page address, 6-bit (63). More and end will wrap around | ||
| + | // But data can be maximum of 28 bytes, because the Wire library has a buffer of 32 bytes | ||
| + | void i2c_eeprom_write_page( int deviceaddress, unsigned int eeaddresspage, byte* data, byte length ) { | ||
| + | Wire.beginTransmission(deviceaddress); | ||
| + | Wire.write((int)(eeaddresspage >> 8)); // Address High Byte | ||
| + | Wire.write((int)(eeaddresspage & 0xFF)); // Address Low Byte | ||
| + | byte c; | ||
| + | for ( c = 0; c < length; c++) | ||
| + | Wire.write(data[c]); | ||
| + | Wire.endTransmission(); | ||
| + | delay(10); // need some delay | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | byte i2c_eeprom_read_byte( int deviceaddress, unsigned int eeaddress ) { | ||
| + | byte rdata = 0xFF; | ||
| + | Wire.beginTransmission(deviceaddress); | ||
| + | Wire.write((int)(eeaddress >> 8)); // Address High Byte | ||
| + | Wire.write((int)(eeaddress & 0xFF)); // Address Low Byte | ||
| + | Wire.endTransmission(); | ||
| + | Wire.requestFrom(deviceaddress, 1); | ||
| + | if (Wire.available()) rdata = Wire.read(); | ||
| + | return rdata; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | // should not read more than 28 bytes at a time! | ||
| + | void i2c_eeprom_read_buffer( int deviceaddress, unsigned int eeaddress, byte *buffer, int length ) { | ||
| + | Wire.beginTransmission(deviceaddress); | ||
| + | Wire.write((int)(eeaddress >> 8)); // Address High Byte | ||
| + | Wire.write((int)(eeaddress & 0xFF)); // Address Low Byte | ||
| + | Wire.endTransmission(); | ||
| + | Wire.requestFrom(deviceaddress, length); | ||
| + | //int c = 0; | ||
| + | for ( int c = 0; c < length; c++ ) | ||
| + | if (Wire.available()) buffer[c] = Wire.read(); | ||
| + | } | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
2017年1月9日 (一) 14:31的最新版本
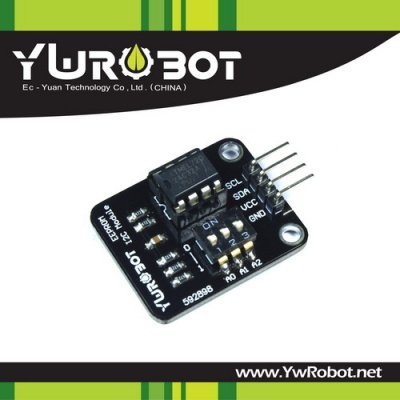
产品参数
- 尺寸:31*20.5mm
- 芯片:AT24C32
- 电压:5V
- 输入:数字电平
- 接口:I2C
- 地址:可选择(3位拨码开关控制)
- 平台:Arduino、单片机
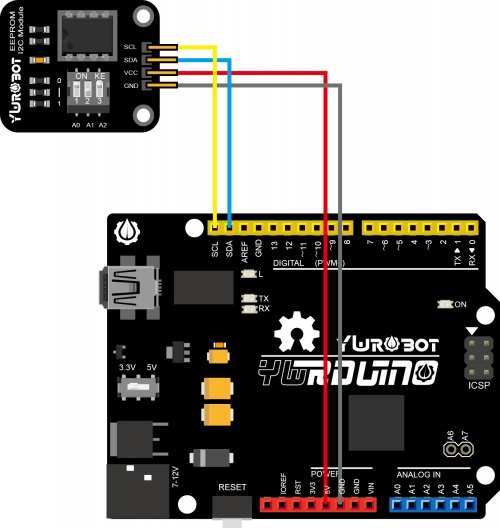
使用教程
样例代码
#include <Wire.h>
#define EEPROM_ADDR 0x57 // I2C Buss address of 24LC256 256K EEPROM
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // join I2C bus (address optional for master)
Serial.begin(9600);
// TESTS FOR EACH FUNCTION BEGIN HERE
Serial.println("Writing Test:");
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { // loop for first 20 slots
i2c_eeprom_write_byte(EEPROM_ADDR, i, i + 65); // write address + 65 A or 97 a
Serial.print(". ");
delay(10); // NEED THIS DELAY!
}
Serial.println("");
delay(500);
Serial.println("Reading Test:");
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { // loop for first 20 slots
Serial.print(i2c_eeprom_read_byte(EEPROM_ADDR, i));
Serial.print(" ");
}
// setup for page tests . . .
byte PageData[30]; // array that will hold test data for a page
byte PageRead[30]; // array that will hold result of data for a page
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) { // zero both arrays for next test
PageData[i] = 0;
PageRead[i] = 0;
}
Serial.println("");
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) PageData[i] = i + 33; // fill up array for next test char 33 = !
Serial.println("Writing Page Test:");
i2c_eeprom_write_page(EEPROM_ADDR, 100, PageData, 28 ); // 28 bytes/page is max
Serial.println("Reading Page Test:");
i2c_eeprom_read_buffer( EEPROM_ADDR, 100, PageRead, 28);
for (int i = 0; i < 28; i++) {
Serial.print(PageRead[i]); // display the array read
Serial.print(" ");
}
}
void loop()
{
}
void i2c_eeprom_write_byte( int deviceaddress, unsigned int eeaddress, byte data ) {
int rdata = data;
Wire.beginTransmission(deviceaddress);
Wire.write((int)(eeaddress >> 8)); // Address High Byte
Wire.write((int)(eeaddress & 0xFF)); // Address Low Byte
Wire.write(rdata);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
// Address is a page address, 6-bit (63). More and end will wrap around
// But data can be maximum of 28 bytes, because the Wire library has a buffer of 32 bytes
void i2c_eeprom_write_page( int deviceaddress, unsigned int eeaddresspage, byte* data, byte length ) {
Wire.beginTransmission(deviceaddress);
Wire.write((int)(eeaddresspage >> 8)); // Address High Byte
Wire.write((int)(eeaddresspage & 0xFF)); // Address Low Byte
byte c;
for ( c = 0; c < length; c++)
Wire.write(data[c]);
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(10); // need some delay
}
byte i2c_eeprom_read_byte( int deviceaddress, unsigned int eeaddress ) {
byte rdata = 0xFF;
Wire.beginTransmission(deviceaddress);
Wire.write((int)(eeaddress >> 8)); // Address High Byte
Wire.write((int)(eeaddress & 0xFF)); // Address Low Byte
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(deviceaddress, 1);
if (Wire.available()) rdata = Wire.read();
return rdata;
}
// should not read more than 28 bytes at a time!
void i2c_eeprom_read_buffer( int deviceaddress, unsigned int eeaddress, byte *buffer, int length ) {
Wire.beginTransmission(deviceaddress);
Wire.write((int)(eeaddress >> 8)); // Address High Byte
Wire.write((int)(eeaddress & 0xFF)); // Address Low Byte
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(deviceaddress, length);
//int c = 0;
for ( int c = 0; c < length; c++ )
if (Wire.available()) buffer[c] = Wire.read();
}
更多
[YWRobot产品资料下载]